Composite vector formulation for multiple siRNA delivery as a host targeting antiviral in a cell culture model of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection†
Abstract
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a major cause of chronic liver disease and cancer worldwide. RNA interference (RNAi)-based gene therapies have emerged recently as a promising tool to treat chronic viral infections. Indeed, small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) provide an opportunity to target host factors required for the viral life cycle. In this study, we evaluated a novel nanovector-based approach for siRNA delivery in a model of chronically infected hepatic cells. We designed original composite nanoparticles by coating the calcium phosphate core with siRNAs targeting HCV host-factors and pyridylthiourea-grafted polyethyleneimine (πPEI). Using combinations of different siRNAs, we observed an efficient and prolonged decrease of HCV replication. Moreover, we showed that the layer-by-layer technique of coating applied to our nanoparticles triggers a sequential release of siRNAs acting on different steps of the HCV life cycle. Together, our results demonstrate the efficacy of these nanoparticles for siRNA delivery and open new perspectives for antiviral therapies.
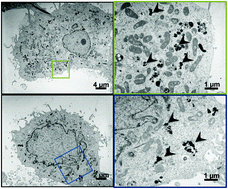

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...