Enhanced performance of doped BiOCl nanoplates for photocatalysis: understanding from doping insight into improved spatial carrier separation†
Abstract
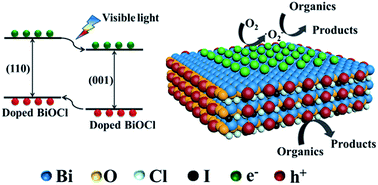
The spatial carrier separation of semiconductor photocatalysts with different crystal facets has been utilized for improving photocatalytic efficiency. However, the efficiency of spatial carrier separation is restricted in these facet-based semiconductor photocatalysts. Herein, we aim to steer spatial separation of photoexcited carriers by implementing a doping strategy and select BiOCl nanoplates as a model photocatalyst to investigate spatial carrier separation and photocatalytic performance. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy shows that doped BiOCl single crystalline nanoplates have (001) crystal facets on their top and bottom surfaces, while they have (110) crystal facets at their four side surfaces. The photoelectrochemical results show that doping enhances the separation efficiency of the photoexcited carriers. Meanwhile, the phenomenon that the valence band decreases gradually while photocatalytic degradation efficiency increases with increasing dopant concentration implies that the increase of photocatalytic efficiency originates from the effective separation of the photoexcited carriers. Furthermore, photodeposition results of BiOCl and doped BiOCl nanoplates indicate an enhanced spatial separation of photoexcited electrons and holes between (001) and (110) crystal facets. The doped BiOCl nanoplates exhibit significant efficiency for pollutant degradation under visible light. The results obtained demonstrate the rational design of spatial carrier separation with different crystal orientations for more efficient solar-driven photocatalytic conversion.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...