Effects of adhesives on the electrochemical performance of monodisperse LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C microspheres as cathode materials for high power lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
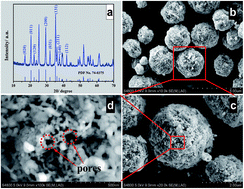
A facile co-precipitation approach combined with spray-drying and high-temperature calcinations was developed to synthesize LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C microspheres on a large scale. With an open porous structure, these microspheres are composed of nanoparticles coated with a carbon layer. The electrochemical performances of a LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C cathode were investigated with a water-soluble adhesive, polyacrylic latex (LA133), and compared with the commercial polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF). The results show that LA133 makes better distribution between the microspheres and acetylene black with a larger and closer contact and stronger adherence. The testing results show that the LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C demonstrates a reversible capacity of 161 mA h g−1. The electrodes with the LA133 adhesive attain higher discharge capacities than the electrodes with PVDF at a large current density, and deliver a long cycle life of 500 cycles at 5C with an excellent capacity retention ratio of 70.5% at room temperature. Even at a low temperature of 0 °C, the LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C electrodes with LA133 retain a capacity of 117 mA h g−1 and stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...