Fabrication of thermo-responsive polymer functionalized reduced graphene oxide@Fe3O4@Au magnetic nanocomposites for enhanced catalytic applications†
Abstract
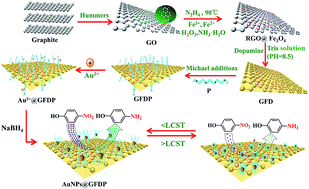
A novel strategy was developed to fabricate thermo-responsive copolymer functionalized reduced graphene oxide@Fe3O4@Au magnetic nanocomposites (Au NPs@GFDP) for highly efficient catalysis. Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) on reduced graphene oxide (RGO@Fe3O4) were obtained via a one-pot chemical functionalization method. RGO@Fe3O4 was coated with dopamine (DA) to generate polydopamine (PDA) modified RGO@Fe3O4 (GFD) through a combination of mussel inspired chemistry of dopamine in a weakly alkaline aqueous solution. The thermo-responsive polymer of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-2,3-epithiopropyl methacrylate) P(NIPAM-co-ETMA) (P) was synthesized via a reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization and was facilely grafted onto the surface of GFD through a Michael addition reaction. The final gold nanoparticle (Au NP) functionalized GFDP nanocomposites were obtained through in situ reduction of gold precursors in GFDP solution using the episulfide groups of P(NIPAM-co-ETMA) as a ligand. The Au NPs@GFDP nanocomposite exhibited excellent dispersibility and stability in aqueous solutions. More importantly, the obtained nanocomposite also displayed easy recyclability because of the existence of Fe3O4 NPs and a higher catalytic efficiency for the reduction of nitrophenols over the Au NPs@RGO@Fe3O4 and Au NPs@GO without polymer modification. Au NPs@GFDP modified with PNIPAM also exhibited excellent temperature-responsive behavior for the catalytic reduction of nitrophenol. Therefore, the strategy described in this work may be of great potential for various industrial catalytic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...