The ionic strength dependent zeta potential at the surface of hexadecane droplets in water and the corresponding interfacial adsorption of surfactants†
Abstract
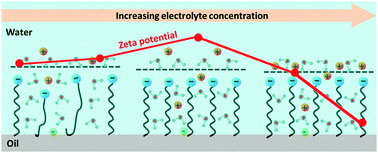
An anomalous maximum in the ionic strength dependent electrophoretic mobility curves has been observed in previous reports from particles dispersed in colloids. This maximum has been considered anomalous because it is contradictory with the Gouy–Chapman model. The existence of such a maximum has been attributed to specific ionic adsorption, a hairy layer at the surface, or the effect of the anomalous change of surface conductivity in different studies. It was also pointed out that the O'Brien–White approach based on the Gouy–Chapman model could be used to understand this maximum in electrophoretic mobility curves and lead to understandable zeta potential curves. This implied that the observed maximum was actually not “anomalous”. In this work we report our simulation of ionic strength dependent zeta potential curves based on the O'Brien–White approach and experimental studies of the ionic strength dependent electrophoretic mobility of the hexadecane droplets in the hexadecane–water emulsions at different pH or in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate at varied concentrations. In some cases, the simulation shows that the calculation with the O'Brien–White approach does change the trend in the concerned ionic strength dependent curves. However, the simulation in some other cases also leads to similar trends in the ionic strength dependent electrophoretic mobility curves and zeta potential curves. In the experiments, both the existence and non-existence of such a maximum were observed and demonstrated to be system dependent. The corresponding molecular structure of the oil–water interface was then discussed with the analyses of the zeta potential curves and second harmonic generation signals recorded at the hexadecane–water interface.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...