Complexation and synergistic boundary lubrication of porcine gastric mucin and branched poly(ethyleneimine) in neutral aqueous solution†
Abstract
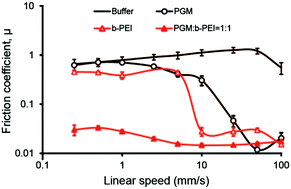
Lubrication of soft polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomer interfaces was studied in aqueous mixtures of porcine gastric mucin (PGM) and branched polyethyleneimine (b-PEI) at neutral pH and various ionic strengths (0.1–1.0 M). While neither PGM nor b-PEI improved lubrication compared to polymer-free buffer solution, their mixtures produced a synergistic lubricating effect by reducing friction coefficients by nearly two orders of magnitude, especially at slow sliding speed in the boundary lubrication regime. An array of spectroscopic studies revealed that small cationic b-PEI molecules were able to strongly bind and penetrate into large anionic PGM molecules, producing an overall contraction of the randomly coiled PGM conformation. The interaction also affected the structure of the folded PGM protein terminals, decreased the surface potential and increased light absorbance in PGM:b-PEI mixtures. Adding an electrolyte (NaCl) weakened the aggregation between PGM and b-PEI, and degraded the lubrication synergy, indicating that electrostatic interactions drive PGM:b-PEI complexation.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...