Deconvoluting the influences of 3D structure on the performance of photoelectrodes for solar-driven water splitting†
Abstract
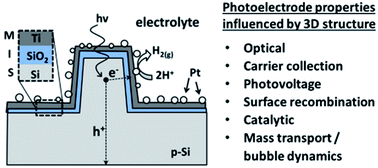
Three-dimensionally (3D) structured photoelectrodes offer a number of potential benefits for solar fuel production compared to conventional planar photoelectrodes, including decreased optical losses, higher surface area for catalysis, easier removal of product species, and enhanced carrier collection efficiency. However, 3D structures can also present challenges, such as lower photovoltage and larger surface recombination. Quantifying and understanding the advantages and disadvantages of 3D structuring can maximize benefits, but this goal is not trivial because the factors that affect photoelectrode performance are intertwined. In this article, we provide an overview of the benefits and challenges of using 3D photoelectrode structures and present a systematic approach for deconvoluting the most common effects of 3D structure on photoelectrode performance. As a basis for this study, metal–insulator–semiconductor (MIS) photoelectrodes consisting of p-Si micro-pillar arrays with well-defined diameter, pitch, and height were fabricated by reactive ion etching (RIE). A general framework for modeling the influences of 3D structure on photoelectrode current–potential performance is presented, and a comparison of the loss mechanisms in 3D and planar photoelectrodes is illustrated using loss analysis diagrams. We expect that most of the measurements and analyses that we demonstrate for MIS photoelectrodes can be applied with equal success to liquid-junction and p–n junction 3D structured photoelectrodes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...