Synthetic upcycling of polyacrylates through organocatalyzed post-polymerization modification†
Abstract
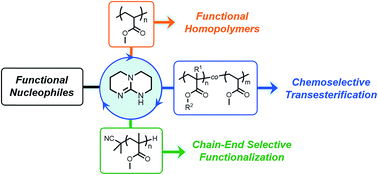
The direct transformation of commercially available commodity polyacrylates into value-added materials was achieved. We demonstrate how 1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene, serving as a nucleophilic catalyst, can be used to catalyze acyl substitution reactions of acrylic polymers in the presence of alcohol and amine nucleophiles. Furthermore, we found that organocatalytic transesterification exhibits high selectivity towards sterically unhindered esters, thus providing a new route towards site-selective acyl substitution of macromolecular materials. Combining this methodology with reversible-deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) techniques such as reversible addition–fragmentation chain-transfer (RAFT) polymerization allowed for the precise functionalization of sterically-differentiated acrylic copolymers and polymeric chain ends. We envision this approach to expedite functional polymer synthesis and provide access to functional macromolecules prepared from inexpensive, hydrolytically-stable polymeric precursors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...