Mechanistic analysis of a copper-catalyzed C–H oxidative cyclization of carboxylic acids†
Abstract
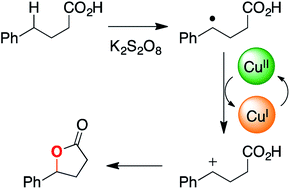
We recently reported that carboxylic acids can be oxidized to lactone products by potassium persulfate and catalytic copper acetate. Here, we unravel the mechanism for this C–H functionalization reaction using desorption electrospray ionization, online electrospray ionization, and tandem mass spectrometry. Our findings suggest that electron transfer from a transient benzylic radical intermediate reduces Cu(II) to Cu(I), which is then re-oxidized to Cu(II) in the catalytic cycle. The resulting benzylic carbocation is trapped by the pendant carboxylate group to give the lactone product. Formation of the putative benzylic carbocation is supported by Hammett analysis. The proposed mechanism for this copper-catalyzed oxidative cyclization process differs from earlier reports of analogous reactions, which posit a substrate carboxylate radical as the reactive oxidant.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...