Toward a mild dehydroformylation using base-metal catalysis†
Abstract
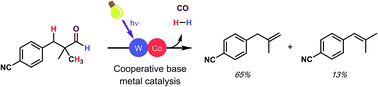
Dehydroformylation, or the reaction of aldehydes to produce alkenes, hydrogen gas, and carbon monoxide, is a powerful transformation that is underdeveloped despite the high industrial importance of the reverse reaction, hydroformylation. Interestingly, nature routinely performs a related transformation, oxidative dehydroformylation, in the biosynthesis of cholesterol and related sterols under mild conditions using base-metal catalysts. In contrast, chemists have recently developed a non-oxidative dehydroformylation method; however, it requires high temperatures and a precious-metal catalyst. Careful study of both approaches has informed our efforts to design a base-metal catalyzed, mild dehydroformylation method that incorporates benefits from each while avoiding several of their respective disadvantages. Importantly, we show that cooperative base metal catalysis presents a powerful, mechanistically unique approach to reactions which are difficult to achieve using conventional catalyst design.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...