Depletion sphere: Explaining the number of Ag islands on Au nanoparticles†
Abstract
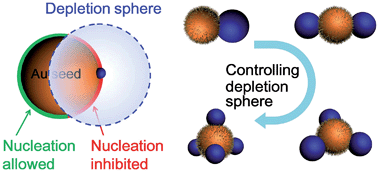
We report multi-site nucleation and growth of Ag islands on colloidal Au nanoparticles. By modifying a single factor, a range of products from Janus nanoparticles to satellite nanostructures are obtained. The identification of these key factors reveals the correlation between the concentration gradient and the choice of nucleation sites. In contrast to the inhibited homogeneous nucleation in the bulk solution, we argue that the non-steady-state concentration gradient plays a critical role in inhibiting nucleation within nanometer distance during the initial stage of growth—an essential but not yet recognized factor in colloidal synthesis. A depletion sphere model was developed, so that the multi-site nucleation is well integrated with the classic theory of nucleation and growth. Alternative explanations are carefully examined and ruled out. We believe that the synthetic know-how and the mechanistic insights can be broadly applied and are of importance to the advance of nanosynthesis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...