Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of N4-benzylamine-N2-isopropyl-quinazoline-2,4-diamines derivatives as potential antibacterial agents
Abstract
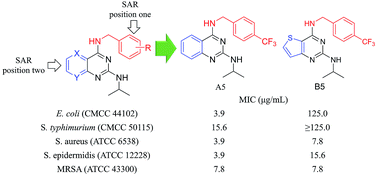
A series of N4-benzylamine-N2-isopropyl-quinazoline-2,4-diamine derivatives has been synthesized and tested for antibacterial activity against five bacterial strains. Twelve different substituents on the N4-benzylamine group have been investigated along with replacement of the quinazoline core (with either a benzothiophene or regioisomeric pyridopyrimidine ring systems). In order to develop structure activity relationships, all derivatives were tested for their antibacterial activities against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus via Kirby–Bauer assays and minimum inhibitory concentration assays. Eight of the most potent compounds against S. aureus and E. coli were also screened against one strain of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), Staphylococcus epidermidis and Salmonella typhimurium to further examine their antibacterial activities. Lead compound A5 showed good activities with MICs of 3.9 μg mL−1 against E. coli, S. aureus and S. epidermidis and 7.8 μg mL−1 against MRSA. Selected front runners were also screened for their DMPK properties in vitro to assess their potential for further development.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...