Synthesis and retention properties of molecularly imprinted polymers for antibiotics containing a 5-nitrofuran ring†
Abstract
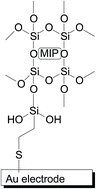
Novel molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) designated for the solid-phase extraction of antibiotics containing a 5-nitrofuran ring (nitrofurantoin and furaltadone) are reported. The synthesis of these MIPs was based on commercial monomers and cross-linking agents capable of forming hydrogen bonds with the template molecules. Thus, the designed MIPs should involve acceptable costs and easier accessibility. Their retention properties were studied by solid-phase extraction (SPE) procedures and the breakthrough curves were evaluated for both imprinted and non-imprinted polymers (NIPs). Due to the presence of adsorption sites created in polymers by imprinting, the MIPs showed a significant difference in the retention property in comparison to NIPs. The MIPs were also immobilized onto a gold electrode surface by entrapment into a silane sol–gel matrix for the development of a sensor based on electrochemical impedance measurements. The good mechanical adherence of the sol–gel matrix on the gold electrode surface was achieved by formation of a self-assembled monolayer using 3-mercaptopropyl trimethoxisilane that acts as an anchoring bridge.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...