Composition analysis of two different PEDOT:PSS commercial products used as an interface layer in Au/n-Si Schottky diode†
Abstract
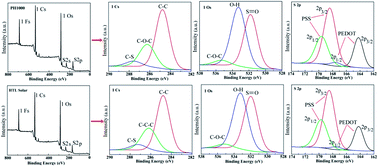
The water based highly conductive transparent poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(4-styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS) polymer is a promising material for many optoelectronic device applications. Chemical composition of PEDOT:PSS plays a key role to improve the performance of the devices. Two different PEDOT:PSS commercial products (PH1000 and HTL Solar) have been used as an interface layer in Au/PEDOT:PSS/n-Si Schottky barrier diodes (SBDs). The effective barrier height increased and the ideality factor decreased with the increase of temperature. Such behavior is attributed to the inhomogeneity and formation of interface dipole affecting electron injection at the interface. The Richardson constant value was obtained from ln(I0/T2) vs. 1000/T plot which is very low from the known theoretical value but the modified Richardson plot ln(I0/T2) − (qσ0)2/2(kT)2 vs. 1000/T gives the closer theoretical value of n-type silicon. The Schottky parameters were extracted from temperature dependent I–V characteristics and successfully explained by thermionic emission (TE) theory. The superiority of HTL Solar product in Au/PEDOT:PSS/n-Si SBDs could be associated for stronger inversion or better passivation on silicon surface compared to PH1000.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...