Establishment of a rapid and sensitive method based on recombinase polymerase amplification to detect mts90, a new molecular target of Mycobacterium tuberculosis†
Abstract
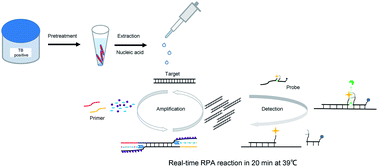
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a significant challenge to public health, especially in developing countries. Failure in early diagnosis and lack of rapid and accurate diagnostic methods lead to ongoing prevalence and transmission of TB. Recently, the recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) technique has made it possible to rapidly amplify and detect nucleic acids without specialized devices. We developed a RPA-based method for identifying Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) by detecting mts90, a more specific target identified in our previous research. Different screening methods were employed for selecting a preferred primer pair of amplification, and probes were confirmed as very fast and reliable tools in the screening of potential primer candidates. The results showed that the mts90 RPA assay was very sensitive and capable of detecting 6 copies of recombinant plasmid containing mts90 sequence per reaction. The assay was specific for detecting MTB, as it did not identify the genomic DNA from other mycobacteria and pathogens. When applied to analyze clinical samples, including sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and tissues, the mts90 RPA assay had a coincidence rate of 96.43% (27/28) compared to the Biochip test, which has been used in clinics for diagnosing TB. The mts90 RPA assay can be completed within 20 minutes at 39 °C without thermal cycling; its simple operation and rapid detection suggest RPA-based MTB assays could be further developed for TB diagnosis in resource-poor settings.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...