Novel 1,2,3-triazolium-functionalized inulin derivatives: synthesis, free radical-scavenging activity, and antifungal activity
Abstract
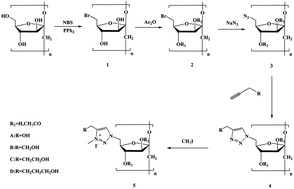
A new class of inulin derivatives possessing 1,2,3-triazolium charged units by associating “click reaction” with efficient 1,2,3-triazole quaternization were designed and synthesized. After the chemical modification, all the inulin derivatives showed good solubility in water, and exhibited excellent bioactivity compared to inulin. In the 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical-scavenging assay, the scavenging activity of 1,2,3-triazolium inulin derivatives (5a–5d) (IC50 0.21–0.29 mg mL−1) was found to be higher than that of inulin derivatives (4a–4d) (IC50 0.58–0.95 mg mL−1) and inulin. 5a–5d (IC50 < 0.01 mg mL−1) also exhibited stronger inhibitory activity against superoxide anion formation than 4a–4d (IC50 0.02–0.09 m g mL−1) and Vitamin C (IC50 0.02 mg mL−1). In the antifungal assays, 5a–5d also inhibited the growth of tested phytopathogens more effectively with inhibitory indices of 43.10–82.56% at 1.0 mg mL−1, compared with 4a–4d and inulin. Based on these data, it is reasonable to propose that the introduction of 1,2,3-triazolium group through chemical modification is significant to enhance the free radical-scavenging activity and antifungal activity of inulin.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...