Electrocatalytic water oxidation at amorphous trimetallic oxides based on FeCoNiOx†
Abstract
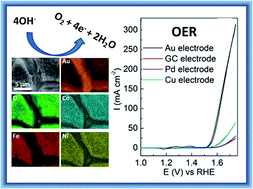
Recently there has been a noticeable shift towards developing amorphous bimetallic or trimetallic oxides for electrochemical water splitting. However, the fabrication of a homogeneous mixed metal oxide electrocatalyst suitable for water electrolysis is not a facile process. Here we introduce an electrochemical synthesis method that is rapid, simple and performed under ambient conditions. Using this approach it is possible to create a catalytically active FeCoNiOxHy amorphous material whose activity is dependent on the nature of the underlying support. The trimetallic oxide is significantly more active than any single or bimetallic oxide combination for the OER. This amorphous catalyst demonstrates not only excellent activity but also stability over extended time periods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...