Significantly improved cyclability of lithium manganese oxide, simultaneously inhibiting electrochemical and thermal decomposition of the electrolyte by the use of an additive†
Abstract
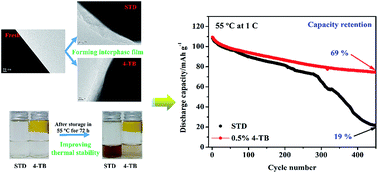
Lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4) is one of the most promising cathodes for lithium ion batteries because of its abundant resources and easy preparation. However, its poor cyclability, especially under elevated temperature, limits its application on a large scale. In this work, it is reported that the cyclability of LiMn2O4 can be significantly improved by applying 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile (4-TB) as an electrolyte additive. Charge/discharge tests indicate that the capacity retention of LiMn2O4 after 450 cycles at 1C and 55 °C in a standard electrolyte, 1 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC/DEC (3 : 5 : 2, in weight), is improved from 19% to 69%. Further electrochemical and physical characterization demonstrates that 4-TB can, on the one hand, be electrochemically oxidized preferentially compared to the standard electrolyte, which generates a protective interphase film on LiMn2O4. On the other hand, 4-TB can effectively combine with protonic impurities, which inhibits the thermal decomposition of the electrolyte. This dual-functionality of 4-TB contributes to the significantly improved cyclability of LiMn2O4.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...