Activation of persulfate by MMIOC for highly efficient degradation of rhodamine B†
Abstract
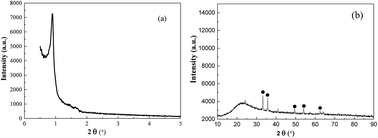
Mesoporous magnetic iron oxide composites (MMIOCs) were successfully prepared using one-step evaporation induced self-assembly using an organic ferrocene surface active agent as the iron source, and innovatively studied as a potential alternative to mesoporous Co3O4 for ammonium persulfate (PS) activation to generate active radicals. MMIOCs were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), N2 adsorption/desorption, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and using a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). Among the different FexOy/PS systems tested, the MMIOC displayed the highest catalytic activity for PS activation, achieving almost complete degradation of 1 mM rhodamine B (RhB) within 120 minutes at 0.2 g L−1 catalyst and 40.0 mM PS. The superior catalytic performance of the MMIOC was ascribed to the combination of iron ions inlayed or embedded in the inner or outer surface, forming catalytically active sites and the magnetic mesoporous structure. Several factors played important roles in controlling the degradation of RhB. The equilibrium between ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) Fe(II) and
Fe(II) and ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) Fe(III) for PS activation in solution ensured continuous generation of the hydroxyl and sulfate radicals, and the latter made the predominant contribution for RhB degradation. Considering its outstanding catalytic activity, excellent reusability and long-term stability, MMIOC could be an ideal catalyst for the degradation of RhB. These results provide an applied solution for disposing of toxic organic wastewater in a relatively available environment, and a scientific foundation for solving refractory organic contaminant related to environmental management.
Fe(III) for PS activation in solution ensured continuous generation of the hydroxyl and sulfate radicals, and the latter made the predominant contribution for RhB degradation. Considering its outstanding catalytic activity, excellent reusability and long-term stability, MMIOC could be an ideal catalyst for the degradation of RhB. These results provide an applied solution for disposing of toxic organic wastewater in a relatively available environment, and a scientific foundation for solving refractory organic contaminant related to environmental management.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...