An asymmetric wettable chitosan–silk fibroin composite dressing with fixed silver nanoparticles for infected wound repair: in vitro and in vivo evaluation†
Abstract
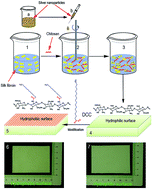
The treatment of large-area infected wounds remains a significant challenge, as there is no effective wound dressing for infected wound healing applicable to clinical applications. In this study, chitosan–silk fibroin composite scaffolds containing silver nanoparticles (AgNP) that underwent asymmetric modification were fabricated for tissue engineering dressings. The scaffolds were prepared from a solution containing a chitosan–silk–fibroin emulsion with added AgNPs using a lyophilization approach and with an asymmetric coating on the surface of one side. Transmission electron microscopy images and laser particle size analysis showed the AgNP distribution, scanning electron microscopy images showed the surface morphology of the dressings, and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry showed the silver content. The asymmetric wettability of the dressings was measured using a contact angle meter. High porosity, good moisture retention capability and appropriate tensile strength were observed by measuring the physical and mechanical properties. Good antimicrobial properties towards various bacteria were observed via in vitro antibacterial effect analysis. Controlled AgNP release by the dressings and their resistance to the infiltration of microorganisms were also observed in our experiments. A highly biocompatible dressing was observed by the MTT assay experiment and subcutaneous sensitization test. Moreover, the effects of the dressings on infected wound healing were measured in mice infected wound models. Analysis of the wound healing rate, bacterial cultures of the exudate, blood samples and histological examination all provided satisfactory results. These results demonstrate that the dressings we prepared offer the potential for infected wound tissue repair and regeneration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...