Activity and stability analysis of covalent conjugated lysozyme-single walled carbon nanotubes: potential biomedical and industrial applications
Abstract
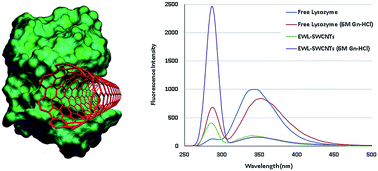
Conjugated protein–carbon nanotubes possess unique physicochemical properties that make them attractive to a wide range of applications. We explored the effects of covalent conjugation of lysozymes with single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) on its activity and stability. Lysozyme was conjugated onto carboxyl-functionalized SWCNTs through carbodiimide method. Post conjugation changes of the enzyme were investigated using fluorescence measurements to generate plots of protein unfolding at 0 and 6 M guanidine hydrochloride (Gn-HCl) concentrations. Free lysozyme showed a remarkable increase in the fluorescence intensity at 287 nm in addition to a red shift from 343 to 352 nm. The emission spectrum of conjugated lysozyme showed a significant increase in the fluorescence intensity at 287 nm and a significant decrease in intensity at 348 nm. These results confirmed that both tryptophan and phenylalanine residues have an important role in the fluorescence bulk of both free and conjugated lysozymes. Kinetic parameters of free and conjugated lysozyme activities (KM and Vmax), optimum pH, thermal and pH stability, and stability in the presence of denaturant agents such as urea and salts were investigated. Changes were observed in KM and Vmax from 4.8 to 5.6 mM and 193 to 197 nmol min−1, respectively. Conjugated lysozyme showed a remarkable increase in pH stability in a range of 3.0 to 10.0 at 70 °C. The results showed first-order inactivation kinetics for both forms of lysozyme with a rate constant of about 0.139 min−1 for 10 minutes of incubation at 70 °C in the presence of KCl and KSCN.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...