A polysaccharide derived from Lentinus edodes impairs the immunosuppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells via the p38 pathways†
Abstract
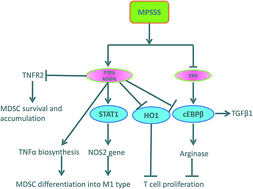
We have previously reported that a novel polysaccharide, MPSSS, from Lentinus edodes can reverse the function of myeloid immune suppressor cell-mediated T cell inhibition and improve the efficacy of cancer therapy, but the mechanisms remained unknown. Here, an immortalized myeloid immune suppressor cell line (MSC2) was used to determine the molecular mechanisms of MPSSS-treatment. The results showed that MPSSS eliminated the immortalized myeloid suppressor cell line (MSC2)-mediated T cell inhibition through downregulating the activation of arginase and decreasing the cell-membrane receptor TNFR2. A p38 inhibitor almost completely prevented the MPSSS-impaired MSC2-mediated T cell inhibition by increasing arginase activity and TNFR2. MPSSS-treated MSC2 cells exhibited increased mRNA levels of TNFα and NOS2 and decreased mRNA levels of TGFβ1, c/EBPβ and HO1. The levels of TNFα were significantly increased after MPSSS stimulation of the MSC2 cells compared with the p38 inhibitor pretreatment group or the control group by ELISA analysis, while TGFβ1 induced the opposite effect under the same treatment condition. Together, these results suggest that MPSSS may reverse the function of the MSC2 cells through p38 activation and ERK suppression and provide a novel anti-cancer strategy by targeting myeloid immune suppressor cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...