Ethyl acetate extract of crabapple fruit is the cholesterol-lowering fraction
Abstract
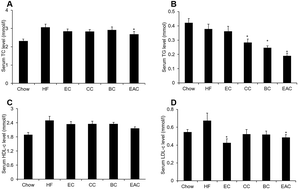
Hypercholesterolemia is highly associated with cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) such as atherosclerosis. Our previous study showed that extracts of crabapple fruit may decrease serum total cholesterol (TC) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. To investigate which bioactive component is responsive for cholesterol-lowering effect in crabapples and whether the component has effects on atherosclerosis, three different chemical fractions were isolated from ethanol extract of crabapples, and obese C57BL/6 mice fed with a high-fat diet and arteriosclerotic low-density lipoprotein receptor deficiency (LDLR−/−) mice fed with a western-diet (WD) were involved in our pharmacological studies. The results showed that ethyl acetate extract of crabapple (EAC) significantly decreased serum TC in both DIO and LDLR−/− mice. EAC also improved obesity, insulin resistance, lipid accumulation in the liver tissue in the DIO mice and prevented atherosclerotic plaque formation in LDLR−/− mice. Mechanistic study showed that EAC increased cholesterol excretion in the feces of DIO and LDLR−/− mice, and elevated CYP7A1 mRNA in HepG2 cell and inhibited cholesterol accumulation in the cell membrane. Our data suggest that EAC may lower serum TC and block atherosclerotic plaque via the inhibition of intestinal cholesterol absorption and TC synthesis in the liver, and EAC may be used as a dietary supplement on hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...