He-Wei granules inhibit chemotherapy-induced vomiting (CINV) in rats by reducing oxidative stress and regulating 5-HT, substance P, ghrelin and obestatin†
Abstract
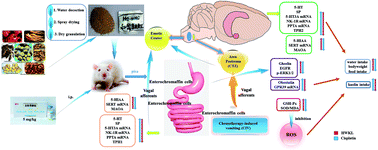
As a common side effect of a variety of chemotherapy drugs, CINV severely limits the clinical use of chemotherapy drugs. Reducing the CINV levels may be useful to improve patient life quality and enable effective use of chemotherapy drugs. In this study, we investigated the protective effects of He-Wei granules (HWKL) against CINV using a cisplatin-induced (5 mg kg−1) pica model. HWKL consists of seven herbs: Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Breit, Zingiber officinale Rosc, Panax ginseng C. A. Mey, Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, Coptis chinensis Franch, Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch, and Ziziphus jujuba Mill. The CINV levels were measured based on the consumption of kaolin. Results showed that HWKL was able to reduce cisplatin-induced increase in kaolin consumption. Cisplatin-mediated increase in tryptophan hydroxylase1 (TPH1), TPH2, 5-hydroxytryptamine 3 receptors (5-HT3AR), neurokinin-1 receptors (NK-1R), 5-HT3AR mRNA, preprotachykinin A (PPTA) mRNA, and NK-1R mRNA was markedly suppressed by HWKL. In addition, cisplatin-induced inhibition of monoamine oxidase (MAOA) and serotonin reuptake transporter (SERT) mRNA was significantly increased after HWKL treatment. HWKL dramatically enhanced appetite by regulating obestatin (OB) and ghrelin (GH); this contributed to further inhibit CINV. The results obtained for G protein-coupled receptor (GPR39) mRNA also confirmed the abovementioned conclusion. HWKL also contributed towards an increase in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and phosphorylation of extracellular regulated protein kinases (p-ERK1/2) to help repair the damaged mucosa; this indicated that HWKL improved the gastrointestinal damage. Overall, our findings suggest that HWKL inhibit CINV by several mechanisms acting simultaneously and provide basic evidence to confirm that HWKL may be useful in clinical situations as a protective agent to prevent CINV. Moreover, 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and substance P (SP) result in inhibition of CINV.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...