New kinetic and mechanistic aspects of photosensitization of iodonium salts in photopolymerization of acrylates
Abstract
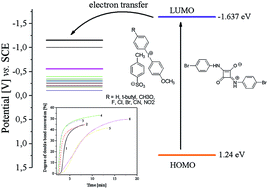
1,3-Bis(p-bromophenylamino)squaraine which functions as an electron-transfer photosensitizer for a wide range of diphenyliodonium salts radical photoinitiators of triacrylate polymerization under UV-blue light irradiation is presented. The functionality of the photosensitizer is determined by the presence of a suitable co-initiator. For this purpose, several different diphenyliodonium salts were used as a source of active species for radical polymerization. The reactivity of the new iodonium salts was studied with ultraviolet-blue light initiated radical polymerization by photo-DSC using squaraine dye as a sensitizer. The iodonium salts functionated as radical initiators bearing different substitution patterns. Electron transfer from the excited state of the sensitizer to the iodonium salt results in initiating radicals. The ability to initiate free radical polymerization of TMPTA by iodonium salts studied is similar. Most of the iodonium salts exhibit no large differences regarding the reactivity in initiation of TMPTA polymerization. However, an introduction of a nitro group in the para position of the phenyl ring of the co-initiator results in a significant increase in the rate of polymerization and degree of monomer conversion. The dye-sensitized photoreaction mechanism of the SQ/I system was also confirmed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...