Larvicidal, super hydrophobic and antibacterial properties of herbal nanoparticles from Acalypha indica for biomedical applications†
Abstract
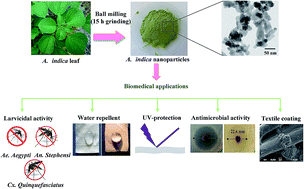
The present study is aimed at developing a biocompatible nanomaterial with excellent medicinal properties using herbs. The herbal nanoparticles were prepared from shade dried leaves of Acalypha indica using the ball-milling technique. The prepared nanoparticles were characterized using X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, particle size analysis, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The amorphous herbal AINPs posses an average particle size distribution of 54 ± 3 nm and a UV-absorption maximum at 434 nm, and are superhydrophobic (151°) in nature. The prepared herbal AINPs were tested for their antimicrobial properties against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Mosquito repellent properties were investigated against three disease vectors, namely, Aedes aegypti, Anopheles stephensi and Culex quinquefasciatus, and showed significant larvicidal activity due to the existence of phytochemical compounds in the herbal nanoparticles. The acute toxicity of the herbal nanoparticles was tested with an in vivo animal model, zebrafish (Danio rerio), to ensure biocompatibility. The observed results confirmed that herbal AINPs play a dominant role in enhancing the medicinal properties for different biomedical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...