Insights into iron induced fouling of ion-exchange membranes revealed by a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring†
Abstract
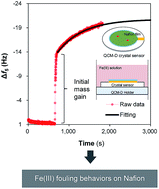
Understanding the mechanisms of multivalent iron interacting with ion-exchange membranes (IEMs) is crucial for the prediction of membrane fouling as well as the development of control strategies. In this study, the adsorption and desorption behaviors of Fe(III) species on a typical IEM, Nafion, were investigated using a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D). The Nafion thin film formed on the crystal sensor surface via a sedimentation method showed a non-rigid structure with a Voigt-based mass concentration of ∼500 ng cm−2 at a Nafion solution injection time of 10 min. Adsorption of Fe(III) species was first assessed using a 10 mM Fe(III) solution, followed by rinsing under different conditions to induce the structural transformation and/or release of Fe(III) from the Nafion film. The QCM-D results suggested that there was a rapid deposition of Fe(III) at the initial stage. It has been found that the ongoing adsorption process exhibiting pseudo-first-order kinetics was associated with the interaction between Fe(III) and the surface functional sites (–SO3H) of Nafion, which consequently retarded the proton transfer. Compared to the rinse with an acidic solution (HCl in ultrapure water, pH of 2.37), the QCM-D results of neutral elution (ultrapure water, pH of 6.50) indicated the hydrolysis of Fe(III) and/or structural transformation of the μ-oxo bridged, Fe–O–Fe.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...