Epoxide functionalization on cholane side chains in the identification of G-protein coupled bile acid receptor (GPBAR1) selective agonists†
Abstract
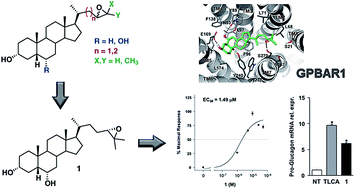
The G-protein coupled receptor of bile acids GPBAR1 is a bile acid receptor that plays an important role in regulating innate immunity, glucose homeostasis and energy expenditure representing an interesting target for the treatment of metabolic and degenerative diseases. A selective control of its activity over the other bile acid-activated receptors is desirable to reduce unwanted effects due to activation of multiple downstream signals regulated by diverse receptors. Here, we report the design and the synthesis of a small series of bile acid derivatives with their side chains decorated with an epoxide ring. We demonstrate that all the compounds selectively activate GPBAR1 in cell-based assays and regulate the expression of pro-glucagon, a canonical GPBAR1 targeted gene in an intestinal endocrine cell line, while have no effect on FXR, LXRα and LXRβ. Finally, we elucidate the binding mode of the most potent compound of this family through molecular modeling studies. Our study contributes to increase the arsenal of bile acid derivatives serving as GPBAR1 modulators, widening the chemical space that can be exploited in drug design.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...