Novel protostane-type triterpenoids with inhibitory human carboxylesterase 2 activities†
Abstract
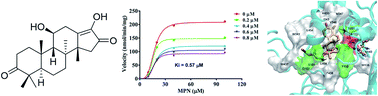
The rhizomes of Alisma orientalis have been used for centuries in China and other Asian countries as an effective herbal remedy. The phytochemical investigation of A. orientalis and biotransformation of two major triterpenoids alisols A (11) and B 23-acetate (13) by Cunninghamella elagans AS 3.2028 and Penicillium janthinellum AS 3.510 have led to the isolation of ten new protostane-type triterpenoids (1–5 and 18–22), including one novel 26-nor-protostane (1) and one unusual 17-nor-protostane (2), together with twelve known analogues. Their structures were determined by 1D and 2D NMR, and HRESIMS spectroscopic analyses. All the isolated compounds were assayed for their inhibitory activities against human carboxylesterase 2 (HCE-2). Compounds 1, 3–9, 12, 14–16, 19, and 20 showed significant inhibitory activities on HCE-2 with IC50 values from 0.51 ± 0.09 μM to 9.45 ± 0.73 μM. The inhibition kinetics of compound 5 toward HCE-2 were established, and its Ki value was determined as 0.57 μM. The interaction of compound 5 with HCE-2 was investigated using molecular docking.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...