In situ ATR-FTIR investigation and theoretical calculation of the interactions of chromate and citrate on the surface of haematite (α-Fe2O3)
Abstract
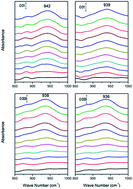
In situ attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy was used to study the molecular kinetics of Cr(VI) reduction by citric acid at the α-Fe2O3–water interface. Both citrate and Cr(VI) were adsorbed to the surface of α-Fe2O3 through the formation of stable monodentate and bidentate complexes. Chromate was potentially reduced by citric acid hydroxyl groups (–COO−) on the α-Fe2O3 surface sites. Monodentate complexes were favoured at pH 4.0 due to strong electrostatic attraction forces between the ions and minerals. Density functional theory was used to calculate the adsorption and interaction processes of Cr(VI) and citrate on α-Fe2O3; the calculations indicated that the adsorption of Cr(VI) or citrate can occur spontaneously and result in the formation of stable complexation structures. However, the co-adsorption of Cr(VI) and citrate on α-Fe2O3 is energetically unstable and leads to the initiation of redox reactions on the α-Fe2O3 surface. These findings have important implications for the fate of chromate in the environment. Therefore, our work describes the molecular mechanism of Cr(VI) reduction by citrate on the surface of α-Fe2O3 for the first time. The results can be correlated to the fate of chromate in the environment in the presence of α-Fe2O3 and low molecular weight organic acids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...