Effect of rapid thermal annealing on crystallization and stress relaxation of SiGe nanoparticles deposited by ICP PECVD†
Abstract
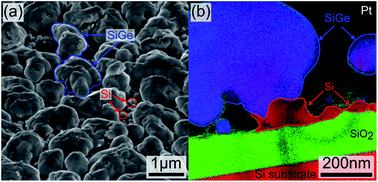
This work demonstrates the viability of direct fabrication utilizing a single (deposition/anneal) process for polycrystalline silicon germanium sub-micro particles. The process combines plasma chemical vapor deposition enhanced with inductively coupled radio frequency plasma at intermediate pressure and high temperature for deposition and rapid thermal annealing as a final step to tune the particles' growth. The deposition process utilizes high plasma density at low kinetic ion energy providing a relatively high deposition rate, favorable for industrial fabrication requirements. Our characterization was performed at two points in the process, post-deposition and post-annealing. Raman spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction were combined to determine the value of stoichiometry x and hence the nature of the obtained compound. Post-annealing, the samples were analyzed by atomic force microscopy, and scanning and transmission electron microscopy to investigate the crystallization, growth kinetics and the strain relaxation of the particles. Our findings show that optimized coarsening of the crystals occurred after annealing at 600 °C for 30 minutes which resulted in internal strain minimization while the composition stoichiometry is kept constant. In addition, the presence of well-defined geometrical facets observed on the surface of SiGe particles, as revealed by atomic force microscopy analyses, suggests that the SiGe particles seem to grow along a preferred crystallographic orientation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...