Self-assembly fabrication, microstructures and antibacterial performance of layer-structured montmorillonite nanocomposites with cationic silica nanoparticles
Abstract
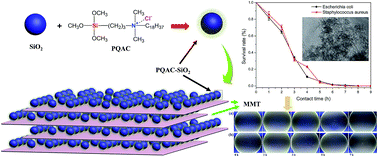
This paper reports the synthesis and antibacterial performance of a novel type of layer-structured montmorillonite (MMT) nanocomposite with cationic silica nanoparticles through an intercalating self-assembly method. The quaternary amine-functionalized SiO2 nanoparticles were first prepared by grafting dimethyloctadecyl [3-(trimethoxysilyl) propyl] ammonium chloride (PQAC) onto the surfaces of silica nanoparticles, and their chemical composition and structure were characterized by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Then, the reactant PQAC–SiO2 nanoparticles were intercalated into the interlayers of MMT through electrostatic self-assembly to achieve the layer-structured MMT/PQAC–SiO2 nanocomposites. The ordered and layered structural characteristics of the resulting nanocomposites were characterized using X-ray diffraction patterns and N2 adsorption–desorption measurements and then confirmed by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The optimum weight ratio of MMT/PQAC–SiO2 nanoparticles was also achieved for the self-assembly fabrication of the nanocomposites on the basis of results mentioned above. The MMT/PQAC–SiO2 nanoparticles gained an excellent thermal stability due to the intercalation of PQAC–SiO2 nanocomposites into MMT and their onset degradation temperature was improved by 40 °C compared to that of PQAC–SiO2 nanoparticles. Most of all, the nanocomposites presented a significant antibacterial effect against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus as the model microorganisms of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, respectively. This type of layered structural nanocomposite is expected to be applied for food packaging and containment of food materials, medical bandages for wound care, removal of environment pollutants like pesticides and phenol, etc.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...