LC-MS-based metabolomics reveals metabolic signatures related to glioma stem-like cell self-renewal and differentiation†
Abstract
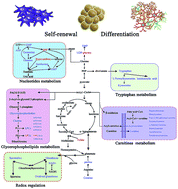
Gliomas are the most common and lethal primary malignant brain tumors. Recent studies implicate an important role for a rare population of glioma stem cells (GSCs) in glioma maintenance and recurrence. New therapeutic strategies are desperately needed requiring insights into the biological and molecular mechanisms underlying the self-renewal and differentiation of GSCs. We now investigate the metabolic signatures of three glioma cell lines with different stemness using a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS)-based metabolomics approach. Cellular metabolites differentially expressed in U87MG stem-like cells (SLCs) relative to U87 malignant glioma cells (GCs) and U87MG stem-like cell differentiation cells (SLCDCs) were identified. The specific and significant alterations including nucleotide metabolism, glycerophospholipid metabolism, glutathione metabolism, carnitine metabolism and tryptophan metabolism were characterized. Cell function assays were further used to evaluate the self-renewal ability of SLCs treated with differential metabolites, indicating that these metabolites are involved in the maintenance of stemness. The results provide valuable information on the association of the significantly altered metabolites and metabolic pathways with SLC self-renewal and differentiation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...