Enhancing menaquinone-7 production in recombinant Bacillus amyloliquefaciens by metabolic pathway engineering†
Abstract
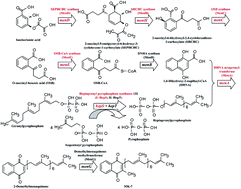
Here, we compared the amino acid sequence of the head structure biosynthetic enzymes in the menaquinone-7 (MK-7) biosynthetic pathway between Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Y-2 and B. amyloliquefaciens W-21 that are distinct in MK-7 production, and investigated the effect of these enzymes on MK-7 production. Sequence analysis showed that six enzymes had undergone non-synonymous substitutions: MenA, MenC, MenD, MenE, MenH and HepS. Overexpression of these enzymes from strain Y-2 in B. subtilis 168 significantly increased the corresponding enzyme activity (increased by ≥500%), which was higher than that from overexpressing these enzymes from strain W-21 (increased by ≈200%). Moreover, the MK-7 content in B. subtilis 168 or B. amyloliquefaciens Y-2 was enhanced by the overexpression of these enzymes from strain Y-2. Note that the overexpression of MenA in B. subtilis 168 increased the MK-7 content up to 1.6-fold, whereas the overexpression of HepS in B. amyloliquefaciens Y-2 led to a greater increase in MK-7 production than that of other enzymes, both in the stilling culture (increased by 93.62%) and in the shaking culture (increased by 93.29%). It follows that the high enzyme activity and high-traffic biosynthetic pathway are beneficial to improve MK-7 production. These results provide a definite theoretical foundation for breeding MK-7 high-yielding strains via metabolic engineering.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...