iTRAQ-based proteomic technology revealed protein perturbations in intestinal mucosa from manganese exposure in rat models
Abstract
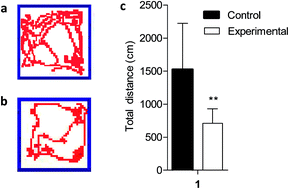
Manganese (Mn) is an essential metal ion as a biological cofactor, but in excess, it is toxic; however, the homeostatic mechanisms of Mn at the cellular level have not been identified. We hypothesized that intracellular Mn can be modulated by proteins that could provide an insight into Mn regulatory mechanisms at the cellular level. Our experiment demonstrated that rats exposed to Mn (200 mg L−1 in water for 5 weeks) showed a significant Mn-induced decrease in total distance traveled, but daily body weight gain and feed intake were not significantly changed. The major organs showed a normal orientation and well defined histological structures without any signs of histopathological changes. We performed a qualitative and quantitative analysis of 3012 proteins for modifiers of cellular Mn content in intestinal mucosa cells by isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ). Following stringent validation assays and bioinformatics, a total of 175 intestinal mucosa proteins were found that may regulate Mn levels under biologically relevant Mn exposures. These proteins are related to pancreatic secretion, protein digestion and absorption, fat digestion and absorption, biosynthesis of amino acids, glycerolipid metabolism, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, mineral absorption associated protein, etc. The identified proteins and biological targets may have potential applications in vivo for modulating cellular Mn content, and will help us understand the homeostatic mechanisms of Mn at the cellular level.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...