Glibenclamide–sulfonylurea receptor 1 antagonist alleviates LPS-induced BV2 cell activation through the p38/MAPK pathway†
Abstract
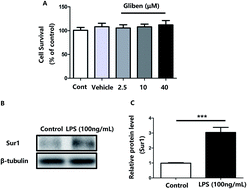
We investigated the anti-neuroinflammatory activity and mechanism of glibenclamide, sulfonylurea receptor 1 (Sur1) antagonist, against LPS-induced microglial activation in vitro. BV2 microglia cells were exposed to LPS (100 ng mL−1). iNOS and COX-2 levels, proinflammatory cytokine mRNA expression, and the p38/MAPK signaling pathway were analyzed by RT-PCR and Western blotting. Pretreatment with glibenclamide (2.5, 10, and 40 μM) inhibited the LPS-induced overexpression of iNOS and COX-2 in BV2 microglia cells. Blocking Sur1 reduced intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. Glibenclamide dose-dependently (2.5, 10 μM) decreased LPS-induced over-expression of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, and alleviated the intracellular calcium accumulation in LPS-treated BV2 microglia cells. Moreover, glibenclamide diminished the LPS-induced phosphorylation of p38/MAPK, SB203580, a selective p38/MAPK inhibitor, significantly potentiated glibenclamide-caused inhibition of the expression of iNOS and COX-2 in LPS-exposed BV2 cells. Glibenclamide–Sur1 antagonist exerts anti-inflammatory activity in murine microglia in vitro by inhibiting the p38/MAPK signaling pathways and proinflammatory responses. Glibenclamide may be developed as a novel agent for suppressing inflammatory responses in the central nervous system.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...