Synthesis, optical properties and residual strain effect of GaN nanowires generated via metal-assisted photochemical electroless etching
Abstract
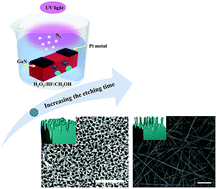
Herein, we report on the studies of GaN nanowires (GaN NWs) prepared via a metal-assisted photochemical electroless etching method with Pt as the catalyst. It has been found that etching time greatly influences the growth of GaN NWs. The density and the length of nanowires increased with longer etching time, and excellent substrate coverage was observed. The average nanowire width and length are around 35 nm and 10 μm, respectively. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) shows a single-crystalline wurtzite structure and is confirmed by X-ray measurements. The synthesis mechanism of GaN NWs using the metal-assisted photochemical electroless etching method was presented. Photoluminescence (PL) measurements of GaN NWs show red-shift PL peaks compared to the as-grown sample associated with the relaxation of compressive stress. Furthermore, a shift of the E2 peak to the lower frequency in the Raman spectra for the samples etched for a longer time confirms such a stress relaxation. Based on Raman measurements, the compressive stress σxx and the residual strain εxx were evaluated to be 0.23 GPa and 2.6 × 10−4, respectively. GaN NW synthesis using a low cost method might be used for the fabrication of power optoelectronic devices and gas sensors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...