Facile synthesis of Fe3O4/MIL-101 nanocomposite as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for degradation of pollutants in Fenton-like system
Abstract
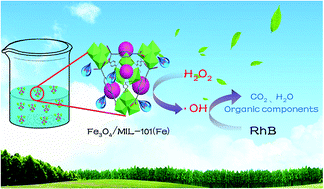
An active Fe3O4/MIL-101 hybrid material was prepared via a simple in situ solvothermal method and characterized as a heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst for Rhodamine B (RhB) degradation. The Fe3O4/MIL-101 exhibited enhanced catalytic performance for RhB degradation in a neutral solution. Under optimized conditions, almost 100% removal of 10 mg L−1 RhB was achieved in 30 min using 0.5 g L−1 Fe3O4/MIL-101 and 20 mM H2O2 at initial pH 7. The reusability of Fe3O4/MIL-101 was also investigated after four runs. On the basis of the characterization of the catalyst, the results of metal leaching, the effects of radical scavengers, and hydroxyl radical (˙OH) determination, it was concluded that RhB is decomposed mainly by the attack of the hydroxyl radical (˙OH), generated by the reaction of Fe2+ species with H2O2. MIL-101 showed a significant synergistic effect with Fe3O4, in which it played the role of a solid-acid catalyst with Lewis acid sites on its surface, ensuring that a Fenton-like reaction occurred in the neutral solution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...