Site-selective biotransformation of ursane triterpenes by Streptomyces griseus ATCC 13273†
Abstract
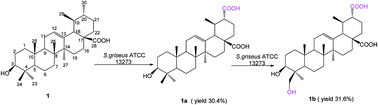
The oxidization of unactivated C–H bonds of pentacyclic triterpenes (PTs) is of great interest for the structural modification of PTs. Herein, we discovered the unique capability of Streptomyces griseus ATCC 13273 to catalyze the site-selective oxidation of the C-30 methyl group to the carboxyl group and hydroxylation of the C-24 methyl group over a range of ursane triterpenes, including ursolic acid (1), 3-oxo ursolic acid (2), and corosolic acid (3). It is noteworthy that while using asiatic acid (4) and madasiatic acid (5), which bear one hydroxyl group on C-23 as substrates, the hydroxylation on C-24 was blocked. As a result, eight new compounds (1a–3a, 5a, 1b–3b and 5b) of the metabolites were isolated and their structures were elucidated based on 1D and 2D NMR and HR-MS data. In addition, the cytotoxicity of substrates and transformed products was preliminarily evaluated by an MTT assay.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...