Experimental and theoretical studies on efficient carbon dioxide capture using novel bis(3-aminopropyl)amine (APA)-activated aqueous 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) solutions†
Abstract
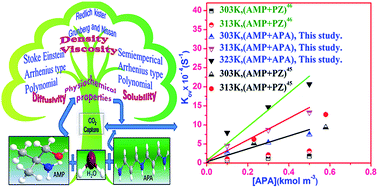
The present study investigates the absorption of CO2, into novel bis(3-aminopropyl)amine (APA)-activated aqueous solutions of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP), using a wetted-wall column absorber. The physicochemical and transport properties of these solvents were measured over a temperature (T) range of 298–323 K and a partial pressure (pCO2) range of 5–15 kPa. APA is used as an activator with molar concentration varying from 0 to 1.1 kmol m−3 while maintaining the total (APA + AMP) concentration to 3.0 kmol m−3. Details on uncertainty analysis of property measurements are provided in order to analyse the kinetics data. The effect of thermodynamic properties on liquid–liquid interactions are discussed and assessed. Following the reaction mechanism of primary and secondary amines with CO2, the reaction mechanism of aqueous APA was described by the zwitterion mechanism. Based on this mechanism, the overall reaction scheme for (APA + AMP + H2O)–CO2 system was established. According to the pseudo-first-order condition, the reaction rate parameters were estimated for the (APA + AMP + H2O)–CO2 system from the kinetics measurement. A substantial enhancement of the reaction rate in comparison to the single AMP solution was observed upon the addition of a small amount of APA to the blend. Furthermore, it was prominent from the parity plot that the model fitted and experimental rate data were in close agreement with each other.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...