Cinobufagin, a bufadienolide, activates ROS-mediated pathways to trigger human lung cancer cell apoptosis in vivo†
Abstract
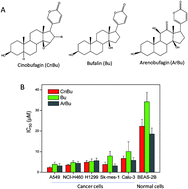
Lung cancer, as the most common malignancy worldwide, is one of the most threatening diseases for human beings. Chan Su, an ethanolic extract from skin and parotid venom glands of the Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor, is widely used as a traditional Chinese medicine in cancer therapy. Bufadienolides are cardiotonic steroids isolated from the skin and parotid venom glands of toad Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor with excellent anticancer activity. Unfortunately, little information about the in vivo effects and action mechanisms of bufadienolides on human lung cancer cells is available. Therefore, in this study, the anticancer activities of Cinobufagin (CnBu), bufalin (Bu) and arenobufagin (ArBu) were evaluated in vivo and in vitro and the underlying mechanisms were elucidated. The results showed that CnBu exhibited higher anticancer efficacy than Bu and AuBu against a panel of five lung cancer cells (A549, NCI-H460, H1299, Sk-mes-1 and Calu-3) with IC50 values ranging from 2.3–6.7 μM. Moreover, CnBu showed much higher selectivity between cancer and normal cells, as suggested by its IC50 value towards BEAS-2B human normal bronchial epithelial cells reaching 22.3 μM. CnBu also significantly inhibited the growth of A549 cells in a dose-dependent manner through anti-migration and anti-invasion. Moreover, CnBu effectively induced apoptosis in A549 cells by triggering caspase activation through intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Treatment of CnBu also significantly caused mitochondrial fragmentation and ROS overproduction in cancer cells. Interestingly, the treatment of ROS scavengers significantly inhibited apoptosis caused by CnBu in A549 cells, further demonstrating the important role of ROS on CnBu-caused cell apoptosis. Moreover, CnBu also exhibited strong in vivo antitumor efficacy by inhibiting the tumor growth through induction of apoptosis in vivo and activation of p53 phosphorylation. In summary, our findings demonstrate the anticancer ability of bufadienolides in vivo against human lung cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...