Exhaled isopropanol: new potential biomarker in diabetic breathomics and its metabolic correlations with acetone
Abstract
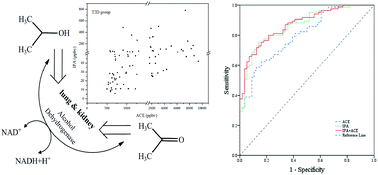
Concomitant findings of acetone (ACE) and isopropanol (IPA) in blood and other biological samples have been reported in diabetic decedents and clinic cases, but exhaled IPA has rarely been studied in breath research. This study aimed to investigate expression of exhaled IPA in diabetes and further explore the correlations between exhaled IPA and ACE, and to evaluate diabetes diagnostic applicability of exhaled IPA in combination with ACE. Exhaled breath samples at one time point from 85 type 2 diabetic patients and 56 healthy controls, and from four healthy individuals after ketogenic diet experiments were analyzed by gas chromatography mass spectrometry coupled with solid phase micro-extraction technique. Concentrations of exhaled IPA in the diabetic group (mean 85.44 ppbv) were significantly higher than those in the healthy group (mean 17.99 ppbv, p < 0.001). Ketogenic diet experiments showed that both IPA and ACE levels were elevated after keto-meals when under fat-consuming metabolic states. And they shared a similar changing pace, even though there was no linear relationship between IPA and ACE in terms of concentrations. The Spearman Correlation Coefficient between exhaled IPA and ACE in diabetes was 0.66, which indicated that IPA and ACE were metabolically correlated. ROC curve analysis showed that IPA possessed promising discriminatory ability (AUC 0.86) with a sensitivity of 75.3% and a specificity of 85.7% for diabetes diagnosis. This research indicates that endogenously produced IPA is a valuable biomarker for noninvasive diabetes diagnosis in breathomics analysis. This work also addressed the speculation that IPA can be metabolized from ACE via the reversible action of alcohol dehydrogenase.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...