Protective effect and mechanistic evaluation of linalool against acute myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats
Abstract
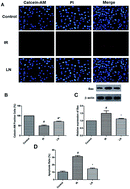
The present study describes the protective effect of linalool against the isoproterenol (ISO)-induced myocardial infarction in adult male Sprague Dawley rats. The results of the study showed that linalool causes considerable improvement of the ischemic heart via number of mechanisms. It has been found that it causes significant reduction in the level of serum LDH and CK-MB levels together with improvement in LVSP, +dp/dtmax and −dp/dtmax 24 h after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R). Use of linalool also showed reduction in the levels of Tn-T (cardiac biomarker) and cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6. Furthermore, significant inhibition of MDA and MPO activities was also reported in the linalool receiving group together with restoration of the decreased SOD and GPx activities. The western blot analysis of linalool was also carried out to determine its effect on the expression of NF-κB. The effect of linalool was found in the results of the histopathology analysis, which confirmed that the linalool treated group showed restoration of microstructural changes in cardiac tissues as compared to the control. Linalool showed significant cell death and apoptosis of H9c2 cells during I/R. It has been found that linalool showed up-regulation of VEGF-B mRNA and protein levels, which promoted the activation of Akt and the inhibition of GSK3β as a possible additional mechanism to exert a cardioprotective effect.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...