Discovery of phosphorodiamidate mustard-based O2-phosphorylated diazeniumdiolates with potent anticancer activity†
Abstract
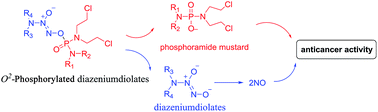
Nitric oxide (NO) has recently joined the clinical arena of cancer therapy because high levels of NO could not only induce cytotoxicity and apoptosis of cancer cells, but also sensitize the cells to chemo- and radio-therapies. Diazeniumdiolates are an important class of NO donors, and the O2-alkylation, arylation and sulfonylation of diazeniumdiolates result in more stable and potent anticancer agents. However, O2-phosphorylation has so far not been reported yet. Herein, we describe the design, synthesis and biological evaluation of a group of phosphorodiamidate mustard-based O2-phosphorylated diazeniumdiolates, 6–9. The most active compound, 7, was comparable, or even more potent, than a known anticancer agent, O2-2,4-dinitrobenzene diazeniumdiolate JS-K, against six cancer cell lines. Furthermore, 7 released larger amounts of NO, caused more significant DNA damage and cancer cell apoptosis than JS-K in the cancer cells. Our findings suggest that this new type of O2-substituted diazeniumdiolate could be potentially applied in the fight against cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...