l-aspartate oxidase magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and l-aspartate bioconversion
Abstract
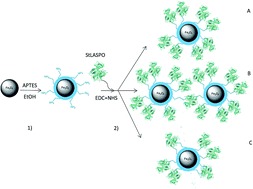
The FAD-containing enzyme L-aspartate oxidase (LASPO) catalyzes the stereospecific oxidative deamination of L-aspartate and L-asparagine functioning under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. LASPO possesses distinctive features that make it attractive for biotechnological applications. In particular, it can be used for the production of D-aspartate from a racemic mixture of D,L-aspartate, a molecule employed in the pharmaceutical industry, for parenteral nutrition, as a food additive and in sweetener manufacture. Since the industrial application of LASPO is hampered by the high cost per enzymatic unit, several attempts have been performed to improve its reusability, such as LASPO immobilization on various matrices. In this context, magnetic nanoparticles (NPs) have recently become available for the immobilization of enzymes. In this work, we have covalently immobilized LASPO from the thermophilic archaea Sulfolobus tokodaii on iron oxide NPs using 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide and hydroxysuccinimide as cross-linking agents. The NP-LASPO system showed a better stability than the free enzyme, was reused five times reaching full L-aspartate conversion and yielded a productivity (>3 μmol per h per unit) similar to that obtained with the free enzyme or with the enzyme immobilized on classical chromatographic supports. The NP-LASPO system can be easily recovered after each cycle. These results indicate that the prepared NP-LASPO system has promising industrial applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...