Colorimetric detection of cholic acid based on an aptamer adsorbed gold nanoprobe†
Abstract
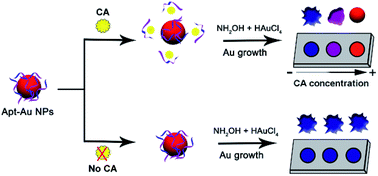
Cholic acid (CA) has been proved as an effective clinical biomarker for disease diagnosis and treatment monitoring. However, traditional CA detection methods are tedious, time-consuming and expensive, and the results cannot be visualized. Herein, we present a facile, low-cost, fast and label-free biosensor platform based on a CA aptamer (48 nt) modified gold nanoprobe for CA detection. CA can bind with the surface-adsorbed CA aptamers competitively and detach the aptamer from the gold nanoparticles (Au NPs). Au NPs modified with aptamers of different densities will grow into morphologically varied nanostructures. The result can be observed visibly and quantified easily with the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) spectra. The detection limit (LOD) was 1 μM, which was lower than the existing colorimetric detection methods based on Au NPs. Furthermore, the affinity between CA and 48 nt aptamer was verified for the first time by MicroScale Thermophoresis (MST) technology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...