Arylidene indanone scaffold: medicinal chemistry and structure–activity relationship view
Abstract
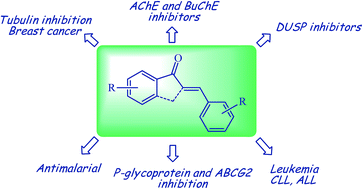
Arylidene indanone (AI) scaffolds are considered as the rigid cousins of chalcones, incorporating the α,β-unsaturated ketone system of chalcones forming a cyclic 5 membered ring. They are generally synthesized from 1-indanone and benzaldehydes via an aldol reaction. The furnished molecules have been explored as inhibitors of cholinesterases towards the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, as tubulin depolymerizing agents, as inhibitors of breast cancer and leukemia, inhibitors of dual specificity phosphatase (DUSP), as antimalarials, and for many other uses. This review is an effort to highlight the biochemical effects of arylidene indanones designed from natural or known drug compounds, discuss their structure–activity relationships (SAR), and correlate them with related chalcones providing insights for further development of this scaffold.
- This article is part of the themed collections: 2018 Open Access Week Collection, 2017 and 2018 RSC Advances Reviews from Around the World and 2017 Review articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...