Polydopamine assisted functionalization of boronic acid on magnetic nanoparticles for the selective extraction of ribosylated metabolites from urine†
Abstract
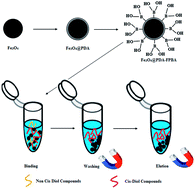
A novel strategy for the rapid and selective extraction of ribosylated metabolites by dopamine assisted functionalization of boronic acid on magnetic (Fe3O4@PDA-FPBA) nanoparticles has been demonstrated under optimized conditions. The study is designed to overcome the drawbacks of dendrimer assisted functionalization of low molecular weight cis-diol compounds, in combination with the advantages of boronic acid affinity towards nucleosides. Magnetic particles provide rapid extraction processing, polydopamine contributes in achieving better functionalization of boronic acid on magnetic particles because of the presence of multiple active sites at terminal groups and boronic acid selectively captures cis-diol compounds via reversible covalent bonding. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) confirm the particle size (80–120 nm). Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) justifies the elemental composition of the material. The BET surface area (64 m2 g−1) is obtained from nitrogen adsorption porosimetry and coating of polydopamine and boronic acid is confirmed by Fourier transform infra-red (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Fe3O4@PDA-FPBA is highly selective with better adsorption capacity (197.3, 183.9, 163.1 and 186.5 μg g−1 for adenosine, cytidine, guanidine and uridine respectively) and recovery for ribosylated metabolites ranging from 87 to 133% for different standards. The magnetic sorbent also extracts 47 endogenous nucleoside metabolites from urine samples of healthy and lung cancer patients. Magnetic separation, combined with superior performance as compared to previously reported materials, makes Fe3O4@PDA-FPBA a promising addition to targeted metabolites analysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...