Inhibitory effect of a genistein derivative on pigmentation of guinea pig skin
Abstract
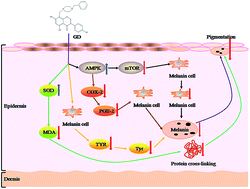
In this study, to improve the properties of genistein, a genistein derivative (GD) was designed and synthesized by combining it with 1-benzylpiperazine. Then, the effects of GD on skin pigmentation in guinea pigs induced by ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation were studied. The guinea pigs were divided into a model group and a GD group. The GD group was coated with different doses of GD for 30 days. Biopsy specimens were taken from the treated skin. Tyrosinase (TYR), malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), as well as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), were detected according to the commercial kits’ protocols. The distribution and secretion of melanin were assayed by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) stain and Fontana-Masson stain methods. The positive staining index of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and AMPK was detected using an immunohistochemical technique (IHC). UVB radiation resulted in a marked increase in the content of TYR, mTOR and MDA, and the expression of COX-2, and promoted pigmentation in guinea pig skins, but decreased the SOD and AMPK levels. The effect of GD was similar to that of arbutin and could reverse these changes and the effect of GD was the best when its concentration was 2%. The SOD and AMPK levels were increased by approximately 46% and 40%, meanwhile, the TYR, mTOR and MDA levels and COX-2 expression were reduced by approximately 30%, 34%, 29% and 30%, respectively. This study shows that GD can be used in the treatment of UVB-induced pigmentation in guinea pigs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...