Adsorption properties of pyridylphenylene dendrimers†
Abstract
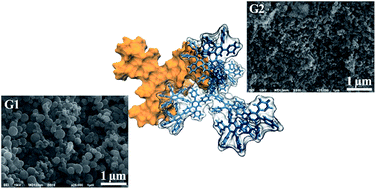
Here we report a sorption and surface properties study of the first three generations of polypyridylphenylene dendrimers. A BET analysis of N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms at 77 K yielded specific surface area values not exceeding 100 m2 g−1, while theoretical estimates predicted large pore volumes and surface areas of thousands of square meters per gram. By means of MD simulations, we showed this difference to be due to the close packing of dendrimers in bulk. T-plot and BJH analyses revealed the mesoporous character of the studied systems, with pore sizes comparable to the diameters of the individual dendrimer molecules. The measured adsorption/desorption isotherms of water vapor on dendrimer generations 1 and 3 implied a chemisorption process involving the formation of hydrogen bonds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...